Explore CityGML
CityGML is an open and vendor-neutral information model for describing the 3D geometry, 3D topology, semantics and visual appearance of urban and landscape objects. This includes, for example, terrain, buildings, water and traffic areas as well as vegetation and land uses. CityGML has been an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) since 2008. In September 2021 CityGML version 3.0 was approved by the OGC.
Content
Why does CityGML exist?
The first applications of 3D city models were often isolated applications, which were realized for special applications and projects. The respective city model was only created for a certain group or a specific area of application, usually limited to a small urban area and only usable with a certain software and hardware. Thus the city model usually became worthless after the project was completed.
With time, the demand for comprehensive 3D city models grew, which could be used throughout the administration as a basis for various projects, tasks and systems. Initially, however, a data model was missing that could cover the various requirements. The solution was seen in the creation of an open data model that combines the different requirements for modeling the city topography.
For this reason, a working group, the Special Interest Group 3D (SIG3D), was formed in Germany in 2002. The SIG3D brought together more than 70 representatives from industry, research and public service to develop a suitable information model.
In 2004 SIG3D submitted its proposal for a data model to the Open Geospatial Consortium. Since August 2008 CityGML has been recognized as a standard of the OGC and version 2.0.0 was released in April 2012. Work on the specification of CityGML version 3.0.0 has been ongoing since then and publication is expected by the end of 2020.
Today CityGML models are an important basis for the construction and use of digital twins. Besides the mere visualization of the city in 3D, they provide access to the city objects as well as their components, relationships and attributes. Only this information makes it possible to use Digital Twins in analyses and simulations and to link them to further information sources such as sensor data.
What are the features of CityGML?
- CityGML is an open information model for describing semantic 3D city and landscape models.
- The information model describes the geometry, topology, appearance and semantics of the essential objects of a city or landscape.
- CityGML defines different levels of detail (LoD-Level).
- CityGML compliant data can be stored in various formats, e.g. XML-encoded or JSON-encoded.
Who uses CityGML?
Every federal state in Germany collects the buildings of its territory as CityGML data set. The federal states submit this data to the central office for house coordinates and house rings (ZSHH) as LoD1 and LoD2 in CityGML format and distribute it themselves to architects, urban planners and similar users. Increasingly, the federal states or individual cities offer their CityGML data as Open Data.
Throughout Europe, the CityGML standard has become so widespread that it is impossible to imagine the 3D city models of most European countries without it, such as Benelux, Scandinavia, Switzerland, Austria, Italy, Spain, France, Great Britain, Turkey, the Czech Republic, Poland, the Baltic States as well as parts of Russia and many other countries.
CityGML is used worldwide in Singapore, USA, Canada, Australia, China, Japan, India and other countries.
What characterizes the relationship of Virtual City Systems to CityGML?
Virtual City Systems is one of the pioneers for the introduction and use of the international CityGML standard. Since its foundation in 2005, the company has been working on the development of software solutions for the creation, storage and use of CityGML. Virtual City Systems was involved in a research project with the Technical University of Berlin, the Hasso-Plattner-Institute Potsdam and the Berlin Senate Administration, in which the first comprehensive 3D city model in CityGML format was developed. The Berlin 3D city model was created parallel to the standardization of CityGML in the years 2007 to 2009. It comprises more than 500,000 buildings on an area of about 890 km². Within the scope of the project, the CityGML standard and the 3D City Database were further developed at the chair of Prof. Dr. Thomas Kolbe, who is considered one of the fathers of the CityGML standard.
From this time not only essential developments of the 3D City Database, which is still the core of our 3D GDI solution, originated, but also some employees who changed over the years from the working group of Prof. Dr. Thomas Kolbe into the company or studied at the TU Berlin. This also includes Dr. Claus Nagel, who is co-editor of the standard and since 2008 is also significantly involved in the development of CityGML as co-chair of the CityGML Standards Working Group at the OGC.
Based on this history, we see ourselves as leading CityGML experts with accumulated CityGML expertise for more than 50 years. We actively support the further development of the CityGML standard and the Open Source 3D City Database.
We think of every software product with the focus on using the strengths of CityGML and exploiting the full range of functions profitably.
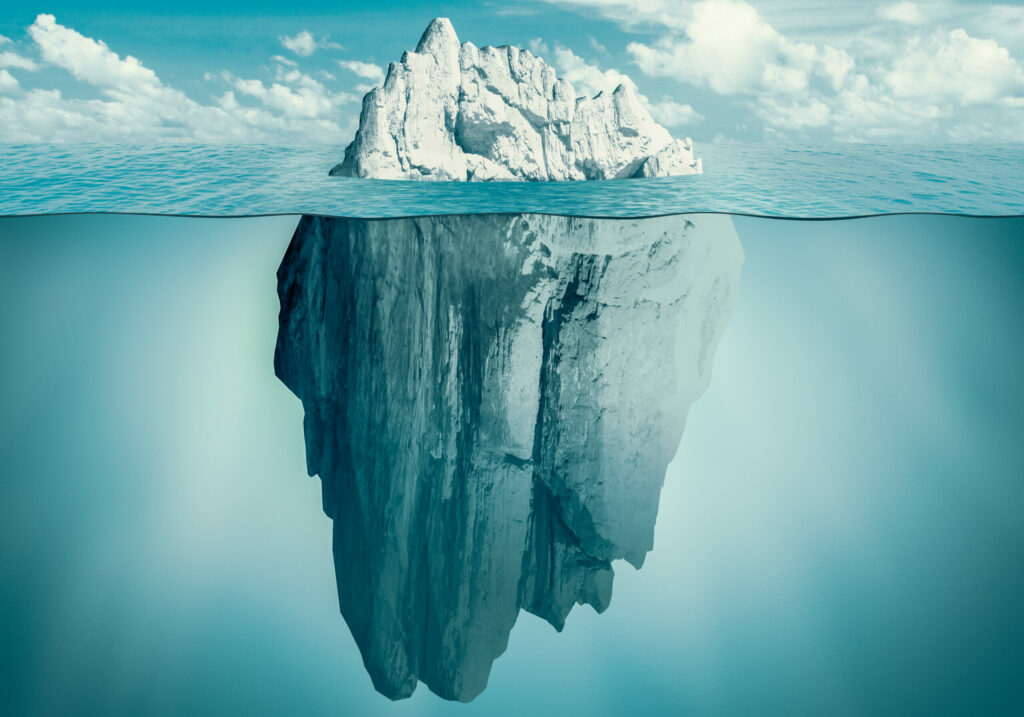
The advantages of CityGML are not only the obvious appearance of ground plan and highly detailed models, but especially the hidden details and attributes. They can be used to develop highly interesting and innovative use cases and can make you think endlessly further.
What are possible application scenarios?
City models for real estate and business development
Publication of solar potential areas and existing plants
Landscape, urban and traffic planning
Flood simulation with display of water levels
Calculation of radio wave or noise propagation
Shading and visibility analyses
CityGML can be summerized in three main points
- Describes the geometry, topology, appearance and semantics of virtual three-dimensional city and landscape models
- Terrain, buildings, water and traffic areas, vegetation and land uses can be defined
- Serves to store, visualize and exchange such models